Soil hydrology field measurements (virtual lysimeters)
These are used to quantify water and solute flows under undisturbed soil, land use and management conditions. They form a cost-effective and flexible alternative to lysimeters.
Concept:
The tension and water content are measured at daily intervals below the zero-flux plane. On arable land this is usually below 3 m of soil, on forest sites below 5 m. From the measured values, a hydraulic conductivity function calibrated to the water balance is generated. Daily seepage rates are calculated applying Darcy’s law and assuming a gradient of unity. Additional water sampling with suction cups enables solute discharges to be quantified.
The methodology was compared with results from lysimeters which had been tested and evaluated as suitable (Dedelow lysimeter analysis at ZALF Müncheberg, Germany and Wagna lysimeter, Joanneum Research in Graz, Austria, Prof. Dr. Johann Fank, Dr. G. Klammler).
Concept of a virtual lysimeter and comparison of lysimeter with field results of the deep seepage dynamics
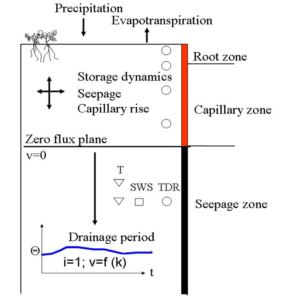
Fig. 1: Virtual lysimeter concept
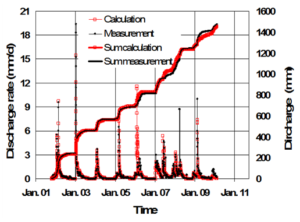
Soil hydrology field studies
(These and other publications are available as pdf including data access at https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Uwe-Schindler and www.zalf.de)
Schindler, U., Eulenstein, F., Müller, L. (2020): Bodenhydrologische Langzeitentwicklung einer Tiefpflug-Sanddeckkultur im oberen Rhinluch. TELMA, Bd. 50, 45-60. (Diese Publikation wurde unter Mitwirkung des Leibniz-Zentrum für Agrarlandschaftsforschung (ZALF) e.V. erstellt)
Schindler, U., Müller, L., Eulenstein, F. (2016) Measurement and evaluation of the hydraulic properties of horticultural substrates. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science 62, 6, 806-818. (Diese Publikation wurde erstellt am Leibniz-Zentrum für Agrarlandschaftsforschung (ZALF) e.V.)
Hohenbrink, T., Lischeid, G., Schindler, U., Hufnagel, J. (2016) Disentangling the effects of land management and soil heterogeneity on soil moisture dynamics. Vadose Zone Journal 15, 1. (Diese Publikation wurde erstellt am Leibniz-Zentrum für Agrarlandschaftsforschung (ZALF) e.V.)
Schindler, U., Müller, L., Eulenstein, F., Dannowski, R. (2008) A long-term hydrological soil study on the effects of soil and land use on deep seepage dynamics in northeast Germany. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science 54, 5, 451-463. (Diese Publikation wurde erstellt am Leibniz-Zentrum für Agrarlandschaftsforschung (ZALF) e.V.)
Schindler, U., Müller, L. (2005) Comparison of deep seepage estimations of a virtual with a real lysimeter by means of TDR-measurements. International Agrophysics 19, 1, 69-73. (Diese Publikation wurde erstellt am Leibniz-Zentrum für Agrarlandschaftsforschung (ZALF) e.V.)
Schindler, U., Müller, L. (2005) Comparison of deep seepage estimations of a virtual with a real lysimeter by means of TDR-measurements. International Agrophysics 19, 1, 69-73. (Diese Publikation wurde erstellt am Leibniz-Zentrum für Agrarlandschaftsforschung (ZALF) e.V.)
Schindler, U. and L. Müller (1998): Calculating deep seepage from water content and tension measurements in the vadose zone at sandy and loamy soils in north-east Germany. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science. 43. 233-243. (Diese Publikation wurde erstellt am Leibniz-Zentrum für Agrarlandschaftsforschung (ZALF) e.V.)
